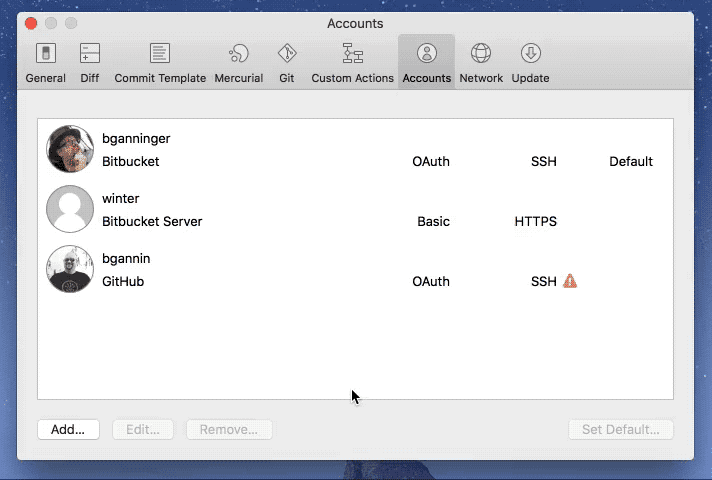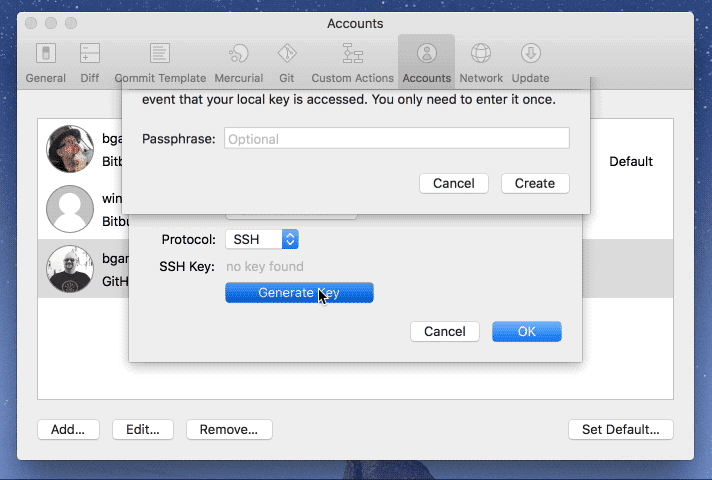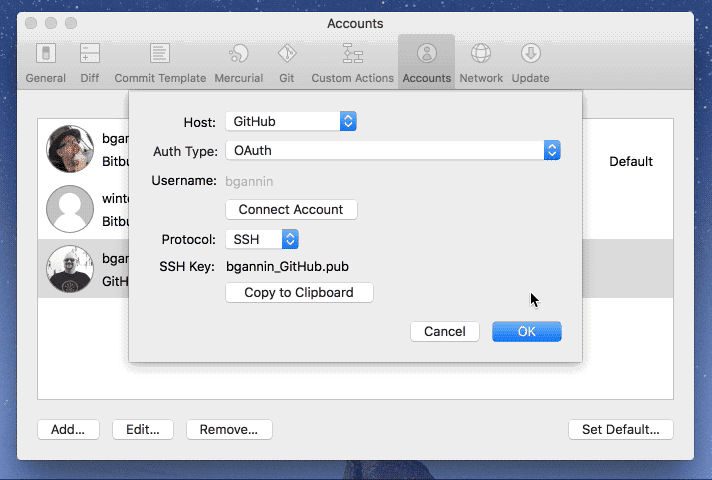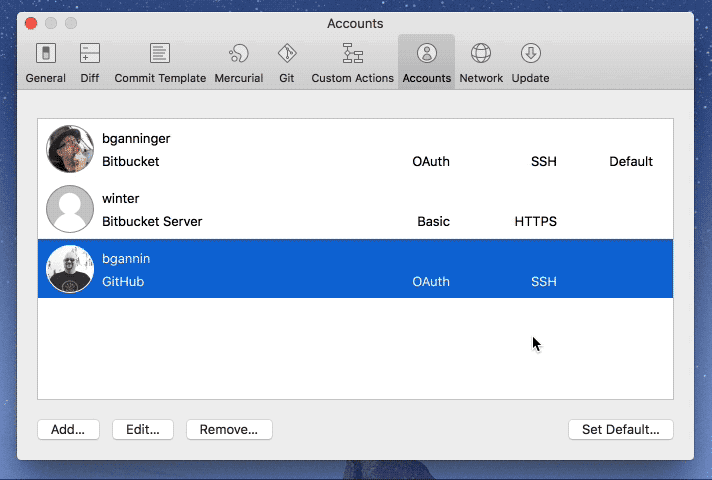
Mac OS X: We recommend installing recommend MacHg to get a good, fast, and native client for Mercurial. MacHg comes bundled with its own Mercurial so you won't have to worry about that. If you already use TortoiseHg on Windows, then you'll be happy to know that you can now install it on Mac OS. This JEP is the index of all JDK Enhancement Proposals, known as JEPs. See JEP 1 for an overview of the JEP Process.
Source archives and binary packages for various systems. See WhatsNew for information on upgrading.
Contents
- Binary packages
1. Binary packages
1.1. Windows
Like TortoiseSVN, we recommend turning off the indexing service on the working copies and repositories, and excluding them from virus scans.
The following installers can be used from Windows XP onwards:
All-in-one installer with TortoiseHg 5.4.2 and Mercurial 5.4.2; comes with Windows Explorer 'shell' integration. | |
MSI installers | Needs admin rights to install, less friendly with manually installed extensions than InnoSetup version. |
5.1 InnoSetup-based installer (exe) | Does not require admin rights to install. |
Python 2 modules | Installs Mercurial source as Python modules, requires Python 2.7 installed. Recommended for hgweb setups and extensions with non-standard dependencies. |
Can install Mercurial, but abstraction layers introduce a potential source of error. Not recommended. | |
Self-contained install that allows easy hacking on the Mercurial source and testing of unreleased versions. |
Most of the above installers are from thg-winbuild, which has nightly builds of Mercurial and TortoiseHg.
1.2. Mac OS X
Mac OS X packages are available on the downloads page
Fink: install with 'fink install mercurial' - 3.3
macports: install with 'sudo port install mercurial' - 3.3
homebrew: install with 'brew install mercurial' - 3.8.1
TortoiseHg for Mac available here - 3.7.3
1.3. Linux (.deb)
Debian
Debian sid (unstable) - 5.5.2
Debian bullseye (testing) - 5.5.2
Debian buster (stable) - 4.8.2
Debian stretch (oldstable) - 4.0
Ubuntu
Ubuntu Groovy - 5.5.1
Ubuntu Focal - 5.3.1
Ubuntu Bionic - 4.5.3
Ubuntu Xenial - 3.7.3
Mercurial (from 1.0 onwards) is packaged for Debian-related distributions as two packages, mercurial and mercurial-common - you only need to care about this if you are downloading .deb files for manual installation - otherwise, APT dependency handling will take care of this for you when you install mercurial.
Another way to get .deb packages is to build them from a Mercurial source repository with make deb (builds on local system) or make docker-- (e.g. docker-debian-stretch or docker-ubuntu-bionic, see contrib/packaging/Makefile).
To get the latest Mercurial version, instead of the old versions listed above, try:
(see the full answer on stackoverflow)
1.4. Linux (.rpm)
Since Mercurial version 3.4, the Mercurial project provides packages for the following systems:
Centos 5 (includes a python2.7 install)
Centos 6
Centos 7
You can download, install and upgrade the packages manually.
You can also add it as a 'yum' package repository and get automatic updates: Add the following file at /etc/yum.repos.d/mercurial.selenic.com.repo and run yum install mercurial.
Mercurial is stable and won't break on automatic updates. Mercurial do however not promise API stability so an update might break extensions or tools using Mercurial internals.
Similar Fedora packages can be built from a Mercurial source repository with commands like make docker-fedora21. 'Unsupported' platforms can use contrib/buildrpm directly.
You can also install the package from your distribution
Mandriva: install with urpmi mercurial - latest revision available
Fedora - latest version is available within few days after release, install with yum install '*mercurial*'
Fedora Projects EPEL for RHEL and CentOS 5: 1.3.1, install with yum install '*mercurial*'
openSUSE - latest version is available shortly after release in the devel:tools:scm repository
Ark Linux - 1.6.2
OpenPKG - 1.4
1.5. Linux (others)
Arch Linux - 4.6.2
Gentoo ebuild: install with emerge mercurial - 4.6.2
T2 SDE - 4.6.2
Slackware - 4.6.2
Optware cross compilation ipk - latest for Python 2.4 and 2.5
1.6. Solaris
unixpackages.com - SPARC/Solaris 2.6-10 packages, x86/Solaris 8-11 packages - 2.3 (8 & 9), 4.2 (10 & 11)
OpenCSW: solaris package mercurial-3.8.2, sparc/solaris, x86/solaris.
1.7. AIX
Mercurial for AIX 5.2 and later - 3.0.2
1.8. BSD
FreeBSD; use pkg_add for installing - 4.6 (on 2018-07-16)
NetBSD packages compiled from pkgsrc - always very up-to-date, currently 4.6.1
1.9. Plan 9 from Bell Labs
To build from source, see: Plan9FromBellLabs
- Binary packages are available from fgb's contrib:
1.10. Other
If you didn't find your favorite distro/package manager above, or if the package version listed on this wiki page seems too old, try https://repology.org/metapackage/mercurial/versions.
2. Source packages
Source code of released versions of Mercurial can be downloaded as usual .tar.gz files at https://www.mercurial-scm.org/release/.
The hg-stable repository leads to stable releases - download snapshot.
The hg repository is the main development repository - download snapshot.
Check DeveloperRepos for other relevant developer repositories where you can clone the hg source.
After getting the source, continue to UnixInstall or WindowsInstall for help with installing.
3. Using pip
Mercurial can also be installed from PyPI with pip, which has shipped with Python since 2.7.9 and 3.4 or can be installed using the instructions on https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installing.html.
To install with pip you must have the same C compiler used to compile Python installed as well as the development headers for Python (typically called python-dev or python-devel on Linux).
You may then install Mercurial simply by executing pip install Mercurial.
4. Using conda
Conda is a cross-platform package manager with a focus on Python. You can install mercurial into a python2.7 conda environment with the following invocation:
This should work on OSX, Windows, and Linux. If you would like to update the conda package, see the instructions at https://github.com/conda-forge/mercurial-feedstock
5. Using easy_install
easy_install is a legacy installation method which has been superseded by pip which should be preferred over easy_install. This method should not be used and is not recommended and will most likely cause conflict with other installs of Mercurial.
Mercurial can also be installed from pypi with easy_install. You will need Python and the C compiler used to build it and easy_install. easy_install might be available in a python-dev or python-setuptools-devel package for your platform or you can grab it from http://peak.telecommunity.com/DevCenter/EasyInstall.
Unable to find vcvarsall.bat fix error with mingw and install mercurial 1.7.3 with python 2.7
With the right prerequisites you can install the latest version of Mercurial using:
You can get Mercurial using Mercurial:
CategoryProject
Francais, 中文, 日本語
Prebuilt binary packages of Mercurial are available for every popular operating system. These make it easy to start using Mercurial on your computer immediately.
The best version of Mercurial for Windows is TortoiseHg, which can be found at http://bitbucket.org/tortoisehg/stable/wiki/Home. This package has no external dependencies; it 'just works'. It provides both command line and graphical user interfaces.
Lee Cantey publishes an installer of Mercurial for Mac OS X at http://mercurial.berkwood.com.

Since Mercurial version 3.4, the Mercurial project provides packages for the following systems:
Centos 5 (includes a python2.7 install)
Centos 6
Centos 7
You can download, install and upgrade the packages manually.
You can also add it as a 'yum' package repository and get automatic updates: Add the following file at /etc/yum.repos.d/mercurial.selenic.com.repo and run yum install mercurial.
Mercurial is stable and won't break on automatic updates. Mercurial do however not promise API stability so an update might break extensions or tools using Mercurial internals.
Similar Fedora packages can be built from a Mercurial source repository with commands like make docker-fedora21. 'Unsupported' platforms can use contrib/buildrpm directly.
You can also install the package from your distribution
Mandriva: install with urpmi mercurial - latest revision available
Fedora - latest version is available within few days after release, install with yum install '*mercurial*'
Fedora Projects EPEL for RHEL and CentOS 5: 1.3.1, install with yum install '*mercurial*'
openSUSE - latest version is available shortly after release in the devel:tools:scm repository
Ark Linux - 1.6.2
OpenPKG - 1.4
1.5. Linux (others)
Arch Linux - 4.6.2
Gentoo ebuild: install with emerge mercurial - 4.6.2
T2 SDE - 4.6.2
Slackware - 4.6.2
Optware cross compilation ipk - latest for Python 2.4 and 2.5
1.6. Solaris
unixpackages.com - SPARC/Solaris 2.6-10 packages, x86/Solaris 8-11 packages - 2.3 (8 & 9), 4.2 (10 & 11)
OpenCSW: solaris package mercurial-3.8.2, sparc/solaris, x86/solaris.
1.7. AIX
Mercurial for AIX 5.2 and later - 3.0.2
1.8. BSD
FreeBSD; use pkg_add for installing - 4.6 (on 2018-07-16)
NetBSD packages compiled from pkgsrc - always very up-to-date, currently 4.6.1
1.9. Plan 9 from Bell Labs
To build from source, see: Plan9FromBellLabs
- Binary packages are available from fgb's contrib:
1.10. Other
If you didn't find your favorite distro/package manager above, or if the package version listed on this wiki page seems too old, try https://repology.org/metapackage/mercurial/versions.
2. Source packages
Source code of released versions of Mercurial can be downloaded as usual .tar.gz files at https://www.mercurial-scm.org/release/.
The hg-stable repository leads to stable releases - download snapshot.
The hg repository is the main development repository - download snapshot.
Check DeveloperRepos for other relevant developer repositories where you can clone the hg source.
After getting the source, continue to UnixInstall or WindowsInstall for help with installing.
3. Using pip
Mercurial can also be installed from PyPI with pip, which has shipped with Python since 2.7.9 and 3.4 or can be installed using the instructions on https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/installing.html.
To install with pip you must have the same C compiler used to compile Python installed as well as the development headers for Python (typically called python-dev or python-devel on Linux).
You may then install Mercurial simply by executing pip install Mercurial.
4. Using conda
Conda is a cross-platform package manager with a focus on Python. You can install mercurial into a python2.7 conda environment with the following invocation:
This should work on OSX, Windows, and Linux. If you would like to update the conda package, see the instructions at https://github.com/conda-forge/mercurial-feedstock
5. Using easy_install
easy_install is a legacy installation method which has been superseded by pip which should be preferred over easy_install. This method should not be used and is not recommended and will most likely cause conflict with other installs of Mercurial.
Mercurial can also be installed from pypi with easy_install. You will need Python and the C compiler used to build it and easy_install. easy_install might be available in a python-dev or python-setuptools-devel package for your platform or you can grab it from http://peak.telecommunity.com/DevCenter/EasyInstall.
Unable to find vcvarsall.bat fix error with mingw and install mercurial 1.7.3 with python 2.7
With the right prerequisites you can install the latest version of Mercurial using:
You can get Mercurial using Mercurial:
CategoryProject
Francais, 中文, 日本語
Prebuilt binary packages of Mercurial are available for every popular operating system. These make it easy to start using Mercurial on your computer immediately.
The best version of Mercurial for Windows is TortoiseHg, which can be found at http://bitbucket.org/tortoisehg/stable/wiki/Home. This package has no external dependencies; it 'just works'. It provides both command line and graphical user interfaces.
Lee Cantey publishes an installer of Mercurial for Mac OS X at http://mercurial.berkwood.com.
Because each Linux distribution has its own packaging tools, policies, and rate of development, it's difficult to give a comprehensive set of instructions on how to install Mercurial binaries. The version of Mercurial that you will end up with can vary depending on how active the person is who maintains the package for your distribution.
To keep things simple, I will focus on installing Mercurial from the command line under the most popular Linux distributions. Most of these distributions provide graphical package managers that will let you install Mercurial with a single click; the package name to look for is mercurial.
Ubuntu and Debian:
Fedora:
OpenSUSE:
Gentoo:
Mercurial Demo Mac Os Download
SunFreeWare, at http://www.sunfreeware.com, provides prebuilt packages of Mercurial.
